Applicability of different paths(1) Simple path
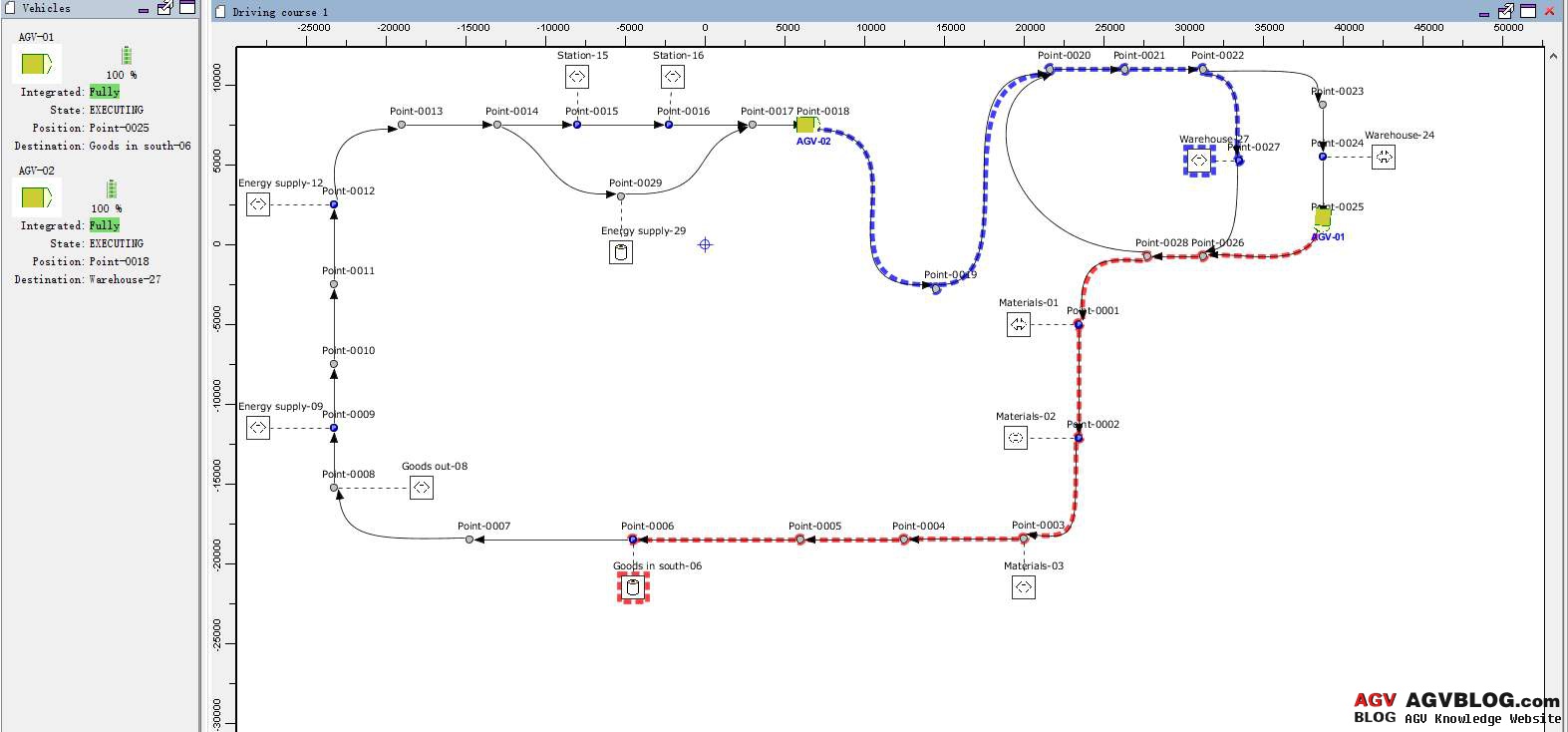
This refers to the AGV driving path with a single line and a small number of intersections, such as straight round-trip and ring-turn. It is suitable for the round-trip transportation of materials between the export of the storage area and the population; for example, the engine of the automobile assembly, the assembly line of the rear axle, etc. Commonly used guidance methods are electromagnetic guidance, magnetic tape guidance, optical guidance, and point guidance.
(2) Complex path
This refers to the path where multiple curves cross, regional dispersion, irregular passages, random assignment of multiple vehicles, and strict requirements for traffic management. It is suitable for the transportation of materials between multiple entrances and exits in the warehouse area and each unit in the production workshop, such as the transportation of auxiliary materials in the cigarette workshop; the supply of various parts in the automobile assembly line. Commonly used guidance methods are inertial guidance and laser guidance.
Applicability of scheduling instructions
(1) Sequential distribution
The AGV accepts the task orders issued by the upper-level scheduling computer according to the queuing order of the waiting time of the empty cars, and assigns them in sequence. It is more suitable for electromagnetic guidance, magnetic tape guidance, optical guidance, and point guidance AGV systems.
(2) Random distribution
The AGV accepts the task orders issued by the upper-level dispatch computer based on random allocation among all waiting empty vehicles. It is more suitable for laser guidance and inertial guidance AGV systems.
(3) Optimized distribution
The AGV accepts the task command issued by the upper scheduling computer to pre-allocate according to the closest distance between the current position of a certain empty vehicle and the task target point, and during this process, if there are more empty vehicles, the system will automatically re Change the instruction, and finally transfer the task to the nearest AGV to execute. It is more suitable for laser guidance and inertial guidance AGV systems.
(4) Special allocation
The AGV accepts the task instructions issued by the upper scheduling computer according to the priority of time, task, conditions, etc., and adjusts and distributes according to the needs. It is more suitable for laser guidance and inertial guidance AGV systems.
summary
(1) The applicability of AGV is closely related to different industries, vehicle models, guidance methods, routes and scheduling requirements. In addition, different environments, occasions, requirements, prices and other factors have a great impact on applicability.
(2) Through the above comprehensive discussion, you can get a general understanding of the overall characteristics and mutual differences of AGV, which has certain reference value for correct understanding, accurate grasp, and flexible application in actual project design.
(3) The discussion in this article is only a hint of the main features, not necessarily complete and accurate, and cannot be used as the sole basis for judgment and selection. It is necessary to analyze specific situations, consider them comprehensively, weigh the pros and cons, and make scientific choices.
(4) In practice, the advantages and disadvantages of an AGV system are not only caused by design factors, but also related to the correct use of the user, and are directly related to the manufacturing process, processing level, assembly debugging, maintenance and so on.


![[Convergence] Analysis of the concept and application of AGV and OMV omnidirectional mobile vehicles](http://www.agvblog.com/wp-content/themes/begin/thumbnail.php?src=http://www.agvblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/3c7f8-0ac06d4b-f4f9-4c27-9341-57dda6d33386.jpg&w=280&h=210&a=&zc=1)
