The purpose of this article is to enable customers to better understand the structural design points of "laser navigation AGV". This article mainly discusses the AGV structure suitable for laser navigation control, and the AGV structure or uncommon structure not suitable for laser navigation. This article does not do discuss.

agv
Common laser navigation AGV: single steering wheel laser forklift, double steering wheel AGV, two-wheel differential AGV, mecanum wheel AGV. The main difference is the chassis structure. Different chassis structures are suitable for different application scenarios.
· Two-wheel differential AGV: suitable for AGV within 500Kg load, which can be rotated in place and cannot be translated.
· Mecanum wheel AGV: suitable for occasions with low running frequency and requiring translation and rotation in any direction at the same time.
· Single steering wheel laser forklift: suitable for loads of more than 1 ton and forklift applications.
· Dual steering wheel AGV: suitable for loads of more than 1 ton, and at the same time it can be translated in any direction.
· According to the way of transportation, it can be divided into: jack-up type, traction rod type, trailer type, roller type, etc.
1. Chassis design
Final chassis performance requirements:
1) In the face of various undulating roads, all driving wheels must be grounded so that the driving wheels can transmit traction force normally, otherwise the phenomenon of suspension and slippage will occur.
2) Under no-load and full-load conditions, the positive pressure transmitted to the drive wheels is large enough to drive the design slope of the climb. Maximum traction force = positive pressure of driving force * friction coefficient of driving wheels. Need to overcome resistance = rolling friction resistance + weight of the component in the slope direction.
Note: For AGV working conditions, it is generally not necessary to do resistance damping similar to cars (except for special scenarios).
2.Introduction to steering wheel
The steering wheel consists of a walking wheel and a steering wheel. Traction wheels are responsible for traction, and steering wheels are responsible for traction.
The steering wheel is divided according to the different installation structures: horizontal steering wheel and vertical steering wheel. The steering wheel load is generally above 500Kg. Walking wheels are generally equipped with brakes.
Drive motor points: DC brushed, AC asynchronous motor, AC synchronous motor. Brushed DC is the earliest motor used by steering wheel manufacturers. The future trend is that AC synchronous motors will become the mainstream.
Foreign steering wheel brand: Italy CFR (Zhejiang Tongpu agent)
Foreign drive brands: American ROBOTIQ, AMC, Copley, American CURTIS Curtis
Domestic steering wheel brands: Giant Wheel, Guangzhou Zhilun, Phoenix Power, etc.
Domestic drive brands: Buco, Xingsong, Beijing Nuotaixin, Asia University Transmission, etc.
3.Introduction of casters
The casters are divided in principle of movement: directional wheels, universal wheels. The specific selection depends on the chassis structure.
The main indicators of casters are: material and bearing capacity.
Different materials have different anti-abrasion capabilities. Materials such as synthetic rubber are relatively soft, have a quiet running performance, and are friendly to the ground. However, it is easy to wear after long use, so it should be replaced in consideration of its service life.
Polyurethane materials can be made into different hardnesses. High hardness polyurethanes have good abrasion resistance, but they have a lot of running noise and are easy to grind the floor paint for a long time.
The universal wheel has a single-wheel structure and a double-wheel structure. It is recommended to use a double-wheel structure at a diameter of 120mm to ensure steering flexibility. Where the AGV space structure permits, the use of large-diameter casters and drive wheels as much as possible will bring the advantages of long life, more obstacles, and greater ability to pass through empty trenches.
The drive wheel generally needs to be customized according to the selected reducer, or the product of the reducer and the drive wheel can be purchased directly.
The reducer for the driving wheel generally adopts a planetary reducer with a flange output. Try not to choose a corner planetary reducer (high price and high noise).
Caster brands: Keshun and Shanghai Yishang.
Reducer brands: Newstar, Dongguan Weige
4. Reducer and drive wheel are integrated
It is recommended to purchase the integrated structure of reducer and drive wheel directly. Compact structure and low failure rate.
5.Single steering wheel structure
This structure has a very wide range of applications on forklifts.
The chassis consists of a steering wheel and two directional wheels. By determining the principle of a plane at 3 points, we know that this structure
It can be directly adapted to various grounds to ensure that the driving steering wheel must land. According to the distribution of the center of gravity of the car, the steering wheel will bear about 50% of its own weight, so the traction is very strong.
Design Points:
1) Caster calculation and selection.
2) Calculation and selection of steering wheel.
3) 2 directional wheels and 1 steering wheel are rigidly connected on the chassis.
6.Double steering wheel structure
The double steering wheel chassis consists of 2 steering wheels and 2 universal wheels. The two steering wheels and the two universal wheels are arranged diagonally. The four wheels will be stressed. In order to adapt to different undulating roads, the two wheels need to be made into a floating structure. Generally, two universal wheels are made to float up and down with springs (or casters with spring floating are directly selected).
Disadvantages of floating structures: When the lateral acceleration is relatively fierce, the body will tilt to a certain extent.
Design Points:
1) Selection design of floating spring.
2) When the spring stiffness is too large, the steering wheel may be suspended or the positive pressure of the steering wheel may be too small under no load.
3) When the spring stiffness is too small, when the vehicle is laterally accelerated at full load, the body tilts sharply.
7.Mclam wheel structure
The Mecanum wheel chassis consists of 4 Mecanum wheels, and the inclination angle of the Mecanum wheels must be arranged as shown in the figure below.
The advantage of this chassis is that it can be translated or rotated in any direction, and it is the chassis with the best flexibility.
Kinematics requires that four wheels must be on the ground at the same time to achieve the ideal motion control. If the four wheels are rigidly connected to the chassis, the principle of determining a plane according to three points can be known, and one of the wheels must be suspended or the force is very small.
To solve this problem, there are two suggestions:
1) The front or back 2 wheels are made of up and down floating structures using springs.
2) Make a set of floating bridge arms with the front or back 2 wheels.
The so-called balanced bridge arm is to fix two wheels on the left and right, and a hinge shaft is fixed to the frame in the middle. Make 2
The wheels merge into one force point. So that all 4 mecanum wheels can be equally stressed.
8.Two-wheel differential drive chassis
This structure is commonly used by service robots and AGVs up to 500KG.
The two-wheel differential drive chassis can be divided into two types: 3-wheel structure and 6-wheel structure.
3-wheel structure: 2 driving wheels, 1 universal wheel. There are applications on the service robot. Because it is a 3-round structure,
So the wheels and the frame can be rigidly connected. The disadvantage is that it takes up a lot of space when rotating in place.
6-wheel structure: 2 driving wheels in the middle, 4 universal wheels in 4 corners of the car. The 6-wheel structure requires special floating treatment to ensure that the two driving wheels are always stressed.
Option 1: Two driving wheels make two independent spring floating structures. The disadvantage is that the requirements for the spring are different between no-load and full-load, resulting in poor adaptability. Especially when climbing a slope above 3 degrees, the drive wheels are easily suspended, resulting in slipping and not being able to climb.
Option 2: Use 3 sets of balanced bridge structure to convert 6 wheels into 3 load points.
Spring floating structure. Scissors or guide shafts can be used to guide up and down.
9, 3 sets of balance bridge chassis
Left driving wheel + left rear universal wheel = 1 driving balance bridge
Right driving wheel + right rear universal wheel = No. 2 driving balance bridge
Left front universal wheel + right front universal wheel = universal wheel balance bridge
10.Lidar
Lidar points: measurement radar, obstacle avoidance radar, and obstacle avoidance radar. According to the application scenario: indoor, outdoor.
The most important parameter of radar is the measurement range. The user first evaluates the detection range of the radar according to the application scenario.
11. LiDAR installation requirements
Lidar points: measurement radar, obstacle avoidance radar, and obstacle avoidance radar.
1. First, determine whether a shock-absorbing bracket is needed based on the radar's anti-vibration and shock capabilities.
2. If you do not need a shock-absorbing bracket, you can use the mounting ear to fix or other on the radar
Fix the screw hole.
3. Obstacle avoidance radar requires a horizontal tilt of about 5 degrees to solve the detection of highly reflective objects.
4. The measurement radar requires the installation plane to be as parallel to the ground as possible to improve the accuracy of ordinary positioning.
Degrees, because if there is a tilt angle, the contour detected by the radar at different positions will have
Large errors will eventually affect the positioning accuracy.
5. It is best to install the laser head below 200mm, about 170mm height.
The best setting (that can be used for safety avoidance and measurement). Choose according to the body structure
The radar can be installed upside down or upside down.
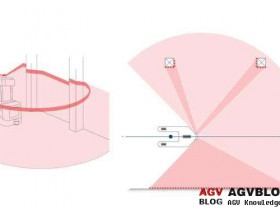
6. On the radar layout, you can choose the middle position of the front of the car or the 4 diagonal points of the car.
If two radars are arranged on the opposite corner of the car, the body can be detected by the lidar 360 degrees,
Thereby no obstacles to avoid obstacles.
7. In different vehicle bodies, the installation of the radar in the x and y directions and the rotation attitude will have errors, which will eventually lead to
The theoretically the same positioning points, the car body has different positions and attitudes. The navigation system can
Set the compensation value of these 3 errors to ensure the consistency of multiple vehicles.
12, obstacle avoidance safety design
First check the safety-related standards to determine the safety level that the vehicle needs to achieve, and then select the safety components and design according to the safety level.
In terms of the safety level of the entire vehicle, generally, the larger the load and the faster the AGV, the higher the safety level requirements.
Safety-related sensors.
1) Lidar for obstacle avoidance.
2) Mechanical anti-collision structure (rope type, rubber switch type). It is recommended to install rubber bumpers on the front and rear of the vehicle.
3) Ultrasonic sensors (not recommended, multiple units are likely to interfere with each other, and no more than one unit is recommended)
4) Infrared obstacle avoidance sensor (easy to be interfered by sunlight)
Electrical requirements:
1) If the strict safety requirements of the European Union are to be met, the yellow safety obstacle avoidance radar must be selected, and the radar obstacle avoidance signal must be associated with the yellow safety PLC and the motor control circuit.
2) Mechanical collision signal, emergency stop switch signal, must use relay to cut off the power of the walking motor driver or connect to
Dedicated STO interface for safety.
13.Charging structure
The AGV is usually designed with a manual charging plug. See if you need automatic charging to decide whether to design an automatic charging structure.
Manual charging plugs can be used: aviation plugs and Anderson plugs. Aviation plug can be selected for charging current below 15A. Anderson plugs are available in sizes up to 350A.
Automatic charging generally uses a brush block structure. Installation methods are: bottom, front, side. It is recommended to use front mounting and a pair of photoelectric switches at the charging site. After AGV is in place, a photoelectric signal is sent out through a photoelectric switch to control the work of the charger.
14. Affiliated executive agency-traction rod mechanism
Traditional towbar mechanisms use springs and mechanical switches. High failure rate. It is recommended to use a non-spring cam structure + photoelectric detection switch.
DC geared motor can choose ZHENG ZGB60FG
It is recommended to use copper sleeves instead of linear bearings for guiding (the linear bearings are easy to be damaged after the guide post collides)
15. Subsidiary executive agency-jacking agency
The jacking mechanism is used for the AGV to drill to the bottom of the cargo, lift the cargo, transport it to its destination, lower it and place it on the shelf, and then the AGV leaves.
Common lifting mechanism.
1) Turbine screw + 4 guide post, using DC brushed or brushless motor, with induction switches installed at the upper and lower limits.
2) Use integrated lead screw.
16. Affiliated executive agency-roller mechanism
Generally, electric drums are used for implementation. Reflective photoelectric switches are designed at the two ends of the drum to detect the material.
Situation in place. A jack-up blocking mechanism can be provided at both ends for blocking articles.
The blocking mechanism may use an electric push rod as an actuator.
The purpose of this article is to enable customers to better understand the structural design points of "laser navigation AGV", and hope to help you.
Author's latest articles
Analysis of the machine 丨 N95 automatic mask machine
Such "dirty" things are actually used as masks
Telecommuting at home during the epidemic has become inevitable. Will it become a trend after the epidemic?
related articles
One of the lightest road helmets in the world
Multiple fault lights on 2019 Nissan Teana sedan overhaul
Want to buy a car after returning to work? Let's take a look at the 4 new heavy vehicles that were launched in March
GAC New Energy's third product is about to launch, offering three battery life versions




![[Depth] The rise of Chinese warehousing robot companies](http://www.agvblog.com/wp-content/themes/begin/thumbnail.php?src=http://www.agvblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/20200904102907-f2f5e.jpeg&w=280&h=210&a=&zc=1)

